Staff Nurse Medical/Surgical ICU (female only)
Company King Faisal Specialist Hospital&Research Center
Salary TBA
Location Jeddah
Job Ref KFSJ28367
Job Description
Staff Nurse Medical/Surgical ICU
Only European passport holders, please, with Western qualifications
Female candidates only and must have current 2 years uninterrupted experience in Medical/Surgical ICU
Candidates must have proof of original Nursing Qualification from country of which they hold passport.
King Faisal Specialist Hospital & Research Center in Jeddah
King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center in Jeddah is a tertiary care hospital in the western region of Saudi Arabia, and plays an important role in setting healthcare standards locally, nationally and internationally. The Hospital is committed as a leader in promoting health, research and education for the wellbeing of patients, staff and community.
Visit Sites http://www.professionalplacement.co.uk/Nursing-Careers/in-Saudi-Arabia/Jeddah/tabid/216/Nursing-Jobs/18025/Nursing/Default.aspx
Portal to the world of medical news and update, where latest information on newest treatment and medicine can be found.
Wednesday, June 30, 2010
Staff Nurse Medical/Surgical ICU (female only)
Sistema Límbico
El sistema límbico es un sistema formado por varias estructuras cerebrales que gestiona respuestas fisiológicas ante estímulos emocionales. Está relacionado con la memoria, atención, instintos sexuales, emociones (por ejemplo placer, miedo, agresión), personalidad y la conducta. Está formado por partes del tálamo, hipotálamo, hipocampo, amígdala cerebral, cuerpo calloso, séptum y mesencéfalo. El sistema límbico interacciona muy velozmente (y al parecer sin que necesiten mediar estructuras cerebrales superiores) con el sistema endócrino y el sistema nervioso autónomo.

Tuesday, June 29, 2010
Tubérculos mamilares
Antibiotics Should Only Be Used For Bacterial Infections
That's mainly the result of fewer young children being seen for ear infections, according to the researchers. But despite a decline overall, prescriptions for broad-spectrum antibiotics, such as azithromycin (Zithromax), and anti-microbial agents known as quinolones have increased, they reported. Such drugs are used to fight more serious infections, such as MRSA and other resistant bacteria.
"There is good news about declining antibiotic use, since inappropriate use of antibiotics can result in bacteria that are resistant to these antibiotics," said Dr. Marie R. Griffin, a professor of preventive medicine at Vanderbilt University Medical Center and a co-author of the study. "However, overuse of powerful antibiotics remains a problem."
"Antibiotics should only be used for bacterial infections, and heavy-duty antibiotics should be saved for serious infections," Griffin said.
Over the last 12 years, she said, use of antibiotics in children has declined 36 percent. "This is mainly due to educational efforts to reduce inappropriate use of antibiotics for viral infections and to a new vaccine -- pneumococcal conjugate vaccine for infants, which has reduced ear infections in children," she said.
For the study, which is published in the Aug. 19 issue of the Journal of the American Medical Association, the researchers looked at the trends in prescriptions for antibiotics from 1995 to 2006, using data from the National Ambulatory Medical Care Survey and the National Hospital Ambulatory Medical Care Survey.
They found that medical visits for ear infections among children younger than 5 declined 17 percent in that time, and antibiotic prescription rates dropped 27 percent.
The study attributed the decrease to a 36 percent reduction in antibiotic prescriptions for respiratory tract infections. Rate of doctor visits for ear infections fell 33 percent over the study period, and rates of antibiotic prescriptions specifically for ear infections fell 36 percent, the researchers found.
Among those 5 and older, doctor visits for respiratory tract infections remained about the same, but antibiotic prescription rates for those infections dropped18 percent. Prescription rates for antibiotics for other conditions for which antibiotics are rarely indicated dropped 24 percent in this age group, the study found.
In the past decade, initiatives in the United States have urged the judicious use of antibiotics, particularly for acute respiratory tract infection, which is a common reason for people to see a doctor and a frequent reason for antibiotic prescriptions, especially for young children, the researchers noted.
The use and misuse of antibiotics can increase the likelihood that bacteria will become resistant to antibiotics. Infections caused by antibiotic-resistant microorganisms have been associated with increased illness, death and substantial costs, the researchers said.
Dr. Stuart B. Levy, president of the Alliance for the Prudent Use of Antibiotics and a professor of medicine, molecular biology and microbiology at Tufts University School of Medicine, said he thinks the trend toward less antibiotic use is encouraging.
"It's a wonderful finding," Levy said. "The message is getting out there. There is a major thrust in the appropriate use of antibiotics -- the realization that if we reduce the use of antibiotics, we will reduce the levels of resistance."
Levy added that it also has become easier for doctors to tell patients they don't need antibiotics.
"Now patients are saying: 'If I don't need the antibiotic, why should I take it?' That is a good sign," he said.
People are getting the message that "antibiotics are not cure-alls, and a consequence of antibiotic usage and misuse is the resistance that emerges," Levy said. ( HealthDay News)
Nanda Nursing Diagnosis By Gordon’s Functional Health Patterns
Download :
Nanda Nursing Diagnosis By Gordon’s Functional Health Patterns
Click Here
and
Click Here
Monday, June 28, 2010
Amígdalas cerebrales

Drugs, Alcohol and HIV/AIDS: A Consumer Guide
Drug Abuse behavior plays the single largest role in the spread of HIV infection in the United States today. This pamphlet answers questions and offers resource and contact information.
Download : Drugs, Alcohol and HIV/AIDS: A Consumer Guide --> click here
Sunday, June 27, 2010
The Science Inside: High Blood Pressure

The Science Inside: High Blood Pressure
This booklet explains what health professionals know about high blood pressure or hypertension, one of the leading causes of heart disease and stroke. It shows how to prevent high blood pressure, as well as how to care for yourself if you have been diagnosed with the disease.
Download The Science Inside: High Blood Pressure : click here
Saturday, June 26, 2010
The Science Inside: Diabetes

The Science Inside: Diabetes
This booklet summarizes what health professionals know about type 2 diabetes — what it is, who is at risk for it, how it can be prevented, and how it is treated. It describes how researchers study the disease and what individuals can do to help reduce the rising number of diabetes cases now affecting millions of children and adults around the country.
Download : The Science Inside: Diabetes click here
Friday, June 25, 2010
Ganglios Basales

Thursday, June 24, 2010
10 Foods That Increase Memory

You already know about 10 great meals that can stimulate the human memory? For those of you who already know it must have felt himself, like what are the benefits, but for you who do not know yet discouraged because in this paper, I will distribute to the 10 types of foods that can stimulate the brain to work better, easier way to create a memory & more intelligent .
The ten types of foods that include :
- Fish
The first is freshwater fish, especially fish such as salmon, trout, tuna, herring, mackerel and sardines.
Basically the fish contains a lot of nutritional content, such as lecithin (choline), phenylalanine, ribonucleic acid, DMAE, tyrosine, vitamin B6, niacin or B3, copper, protein, zinc, omega-3 fatty acid (DHA) and vitamin B12. - Egg
It was no doubt a nutritious eggs contain content such as phenylalanine, lecithin (choline), vitamin E, vitamin B6. - Chicken
Chicken contains phenylalanine, vitamin B6, niacin or B3 & protein. - Banana
Banana is a fruit that contains tyrosine, magnesium, potassium and vitamin B6. - Low Fat Milk Products
These foods contain phenylalanine, tyrosine, slutamin, protein, ALC & vitamin B12. - Avocado
This fruit contains a tyrosine & magnesium. - Soybean
Containing soy lecithin (choline), glutamic acid, phenylalanine, vitamin E, iron, zinc, protein, vitami B6. - Beef Without Fat
Containing phenylalanine, lecithin (choline, glutamic acid, an iron, zinc) - Chicken Liver
Containing vitamins A, B1, B6, B12, protein, iron & tyrosine. - Gandum
Grain lots containing lecithin (choline), glutanik acid, vitamin B6, B1 and E and magnesium.
Thus the ten foods that can improve the performance of the human brain. If we are diligent in taking it so our body butter to be healthy, safe and sound also we will have a brilliant brain.
Cuerpo Estriado

Wednesday, June 23, 2010
How to Find Autism From Babies - Autism Infant Characteristics

Autism Infant characteristics
Patients with autism can be recognized Since Birth - autistic children have some symptoms that can be recognized since they were born. When he was three years old, the symptoms are more evident.
Similarly submitted by Roselyn Saez, children with special needs practitioners, Linguistic Indonesian Council seminar "Your Child Is Special" at Menara Kuningan, Jakarta.
Similarly submitted by Roselyn Saez, practitioners special needs children, autistic patients have several characteristics such as difficulty communicating and socializing. Autism do not know how to express joy or sadness. They also do not know how to communicate.
"An autistic child does not know how to call his mother, they'll hurt himself, hitting him until his mother comes, that's one way they called her mother," said Roselyn.
According to Roselyn, autism often spoke in a monotone and expressionless. Sometimes they repeat the words of other people that they hear, or commonly called echolalia.
Apart from weak communication, autism is often acting weird like always repeat the same activities every day. "For instance, they wear school uniforms. First wear clothes, both wear the pants, the third wearing shoes, always regularly because they are difficult to organize," says Roselyn.
Roselyn also gave an example, an autistic student has no fear of danger. "A student who was two years old I like to go up to the fourth floor, leaned down, just to get a sensation of horror, he did not know it was dangerous," he said.
In addition, children with autism also have excessive obsession with something. For example, they obsess on the numbers, then they will continue to pay attention to the numbers, or obsessing on a rope, they will memaimkan rope continuously. "People with autism are also sensitive to the touch. They can hurt just because of the small touches," he said.
However, there are unique advantages autistic children. They can recall in detail, and accurate information. Their visual memory is also very good and able to concentrate on certain subjects or work in a long period.
Children with autism require special care and handling from an early age. There are several treatment that can be done such as providing specialized education, such as occupational therapy for stroke patient therapy, speech therapy and language therapy, physical therapy to train
their muscles, applied behavioral analysis to help recognize behaviors which positively or negatively, picture exchange communication system, which is a method of learning through pictures, expressing words through pictures that easily captured autism.
Roselyn also said there is no exact cause of autistic children. Could be due to environmental or health patterns of the mother during pregnancy, can also influence gene. "Unkown, is not known precisely because of various reasons," says Roselyn.
Seminar on "Your Child Is Special" introduces some features of children with special needs, education, and how to build a good relationship with them. This seminar was organized by the Indonesian Council in collaboration with the Linguistic Shining Stars, Brass Family and Community Center, and HOPE Worldwide Indonesia.
Adapted from Kompas.com
Sustancia Nigra
Aunque la sustancia nigra aparece como una banda contínua in secciones del cerebro, estudios anatómicos han descubierto que la misma consta realmente de dos partes con conecciones y funciones muy diferentes: pars compacta y pars reticulata. La porción pars compacta sirve como una entrada al circuito de los ganglios basales, suministrando al cuerpo estriado con dopamina. En cambio el pars reticulata de la sustancia negra sirve principalmente como una salida, llevando impulsos nerviosos desde los ganglios basales hacia las otras estructuras nerviosas de la base del cerebro.
Tuesday, June 22, 2010
Papilomavirus: vacunación mediante Gardasil
El Doctor Harald zur Hausen, reciente Premio Nóbel de Medicina por su descubrimiento de que el cáncer de cuello de útero está producido por un virus, afirma que "habría que vacunar al 100% de la población (incluidos los varones) contra el papilomavirus" (El País, 26/10/2008). El Premio Nóbel hace, en la entrevista, afirmaciones tan peregrinas como que está convencido de que los virus pasan de los mamíferos al hombre por comer carne cruda o poco hecha, o que el 21% del los cánceres son de origen infeccioso. Si cada una de estas afirmaciones puede parecer muy cuestionable, el conjunto de ellas hace sospechar sobre los motivos reales de la concesión del Nóbel.
Veamos algunos datos: En España, la mortalidad por cáncer de cuello de útero es de menos de dos mujeres por cada cien mil. El cáncer de cuello de útero está asociado a la falta de higiene y a la pobreza. El país que muestra la mayor incidencia es Haití, el más pobre del mundo, con unas cifras que llegan al 3%, por causa de la "falta de higiene y la promiscuidad", pero sobre todo por la pobreza.
La necesidad de la campaña de vacunación masiva que las autoridades sanitarias están promocionando no se sostiene, simplemente, atendiendo a las cifras de la incidencia de dicho cáncer, pero mucho menos si nos atenemos a sus verdaderas causas. ¿Cuál puede ser, pues, el motivo de semejante desatino? Algo que, posiblemente, "sorprenderá" a los lectores: La avidez de dinero de los laboratorios farmacéuticos que comercializan la carísima vacuna "Gardasil", cuya supuesta eficacia (y lo que es peor, sus posibles efectos) no se podrán comprobar hasta pasados 20 ó 30 años. Los laboratorios Merck emprendieron, el pasado año, una campaña de presión a los políticos de Estados Unidos para que su vacuna se aplicase con carácter obligatorio. En el estado de Texas lo consiguieron e, incluso, Merck hizo una campaña para que las escuelas no admitieran a las niñas de 11 y 12 años que no hubiesen sido vacunadas.
Finalmente, su campaña se suspendió por las protestas sobre su alto costo y por la reacción de las fuerzas conservadoras con el argumento de que la campaña favorecía el sexo prematrimonial. A pesar de la suspensión de la campaña, los beneficios económicos de la vacuna han sido enormes. Ahora, lo intentan en España.
Pero, ¿Cuál es la verdadera relación de los virus con el cáncer? ¿Son causa o son efecto? Hace tiempo que se ha comprobado en algunos tumores que emiten partículas retrovirales.
TIP 48: Managing Depressive Symptoms in Substance Abuse Clients During Early Recovery

This TIP, Managing Depressive Symptoms in Substance Abuse Clients During Early Recovery, provides substance abuse counselors the "what," "why," and "how-to" of working with clients with depressive symptoms and substance use disorders, covering topics such as counseling approaches, clinical settings, cultural concerns, counselor roles and responsibilities, screening and assessment, treatment planning and processes, and continuing care. This TIP also provides administrators information about incorporating the management of depressive symptoms into their substance abuse programs, complete with a systematic approach to designing and implementing a supportive infrastructure. The Literature Review synthesizes the most current knowledge and scientific findings on the topic and is only available online at www.kap.samhsa.gov.
Download click here
Monday, June 21, 2010
Núcleo Caudado

Saturday, June 19, 2010
Treatment for Rheumatic Heart Disease
Specific treatment for rheumatic heart disease will be determined by your child's physician based on :
- Your child's overall health and medical history.
- Extent of the disease.
- Your child's tolerance for specific medications, procedures, or therapies.
- Expectations for the course of the disease.
- Your opinion or preference.
The best treatment for rheumatic heart disease is prevention. Antibiotics can usually treat strep throat (a Streptococcus bacterial infection) and stop acute rheumatic fever from developing. Antibiotic therapy has sharply reduced the incidence and mortality rate of rheumatic fever and rheumatic heart disease.
Children who have previously contracted rheumatic fever are often given continuous (daily or monthly) antibiotic treatments to prevent future attacks of rheumatic fever and lower the risk of heart damage.
If inflammation of the heart has developed, children may be placed on bed rest. Medications are given to reduce the inflammation, as well as antibiotics to treat the Streptococcus infection. Other medications may be necessary to handle congestive heart failure.
If heart valve damage occurs, surgical repair or replacement of the valve may be considered.
Source : http://www.chw.org
Friday, June 18, 2010
Radiology

Radiology is the branch of medicine that uses radioactive substances, electromagnetic radiation, and sound waves to create images of the body, its organs, and structures for the purpose of diagnosis and Female Doctor viewing X-raytreatment. Images can also show how effectively the body and its internal organs and structures are functioning.
Radiology was discovered a little over 100 years ago and has evolved into a high-tech science with state-of-the-art equipment to aid in imaging every aspect of the body.
While there has been concern over the potential harmful side effects associated with the use of radiation, it is believed that the small risks are greatly outweighed by the information gained about patients' conditions and radiology's contribution to medical science.
Radiology offers both diagnostic and therapeutic services. The specialty areas of radiology include the following :
- Diagnostic Radiology - An area of radiology that uses external radiation to produce images of the body, its organs, and other internal structures for medical diagnostic purposes.
- Nuclear Medicine - A specialized area of diagnostic radiology that uses very small amounts of radioactive materials to create an image of the body, its organ functions, and structure, for diagnostic and treatment purposes.
- Therapeutic Radiology (Radiation Oncology) - A specialized area of radiology that uses applications of radiant energy to study, treat, and manage cancer and other diseases.
- Interventional Radiology - A specialized area of radiology that uses various imaging techniques to guide the insertion of small instruments and tools through the body to identify and treat a medical disorder without requiring conventional surgery.
Núcleo lenticular

Thursday, June 17, 2010
Putamen

Wednesday, June 16, 2010
CARE (Constipation and Reflux Evaluation) Program
During the first clinic visit, the pediatric nurse practitioner will obtain a health history, perform a physical exam and formulate an individualized treatment plan with the family. Our approach consists of a combination of education, behavior management and medication interventions that are tailored to meet the unique needs of each child. Some tests and lab work may be completed during the visit; others may need to be scheduled for a different day. Dietitians and psychologists also support the program by providing additional intervention on diet and when behavioral issues interfere with management.
Diagnosis/Conditions treated :
- Abdominal pain with constipation.
- Can't potty train.
- Constipation.
- Encopresis (pooping in pants).
- Reflux – infants under 18 months who do not have feeding issues.
- Difficult, painful or infrequent stooling.
Source : http://www.chw.org/display/PPF/DocID/28105/Nav/1/router.asp
Globo Pálido

Tuesday, June 15, 2010
The Down Syndrome Clinic
We understand that a patient's well-being includes many complex issues and requires a comprehensive, multidisciplinary health care approach. We are connected to a network of local and national resources.
Services for families
Staff at the clinic can provide or help coordinate the following services:
- Family-centered care. Clinics are scheduled monthly, usually the first or second Thursday of the month. Visits are customized to meet the needs and concerns of families. Advanced scheduling is required.
- Second opinions. Patients often have complex issues and families may require a second opinion. We are happy to provide a second opinion and help you prioritize concerns and sort through problems.
- Information and referrals. It is common for people with Down Syndrome to receive care from multiple specialists. The Down Syndrome Clinic staff can provide families with specialist referrals as well updated information on health and wellness topics.
- Training and education. We provide training and education for parents on a variety of health issues.
Services for health care providers
Down Syndrome Clinic staff also can provide support to primary care physicians in making health care decisions affecting children or adult family members with Down syndrome:
- Information and referrals.
- Patient consultation services.
- Education and training for providers.
Source : http://www.chw.org
Tálamo

Monday, June 14, 2010
Hipotálamo
El hipotálamo sintetiza y segrega por lo menos nueve neurohormonas. Este núcleo gris también regula los reflejos gástricos, la presión sanguínea, respuestas inmunológicas y temperatura. Se lo considera el centro integrador del sistema nervioso autónomo dentro del sistema nervioso periférico. También se encarga de realizar funciones de integración somato-vegetativa.

Saturday, June 12, 2010
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) Test
 Intelligence Quotient (IQ) test or most popular called IQ test is a test method that to determine and measuring your personal mental abilities. Whether you are believe or not, this type of test can be a good estimate of intelligence (if you excuse the cultural bias).
Intelligence Quotient (IQ) test or most popular called IQ test is a test method that to determine and measuring your personal mental abilities. Whether you are believe or not, this type of test can be a good estimate of intelligence (if you excuse the cultural bias).IQ test is used not only for children, but also for adults. Everyone has hundreds of specific mental abilities, some can be measured accurately and are reliable predictors of academic and financial success by Iq test. Originally, IQ test was used to detect persons of lower intelligence in order to place them in special position on their job's skill or education programs for the student.
 Actually, IQ tests were designed to compare a child's intelligence to what his or her intelligence "should be" as compared to the child's age. If the child was significantly "smarter" than a "normal" child of his or her age, the child was given a higher score, and if the child scored lower than expected for a child of his or her age, the child was given a lower IQ score.
Actually, IQ tests were designed to compare a child's intelligence to what his or her intelligence "should be" as compared to the child's age. If the child was significantly "smarter" than a "normal" child of his or her age, the child was given a higher score, and if the child scored lower than expected for a child of his or her age, the child was given a lower IQ score.Many of IQ test was offered for the adults to compare an adult's objective results to the objective results of other adults in the same age. So, they can determine and measure their intelligence base on standard's score. These are kind of IQ test ; Mental IQ test, Emotional IQ test, Sexual IQ test, Accurate IQ test, Memory IQ test, Children IQ test, Adult IQ test, School IQ test, Personality IQ test.
Circunvolución Dentada
Circunvolución dentada en corte transversal del cerebro

Thursday, June 10, 2010
Accurate IQ Test
 IQ test also better for an adult, whether for entertaining (exercise their brain) to get personality and intelligence level or to decide which careers, jobs, or professions match their IQ and intelligence. Many of accurate IQ test and personality intelligence tests online, Everyone has hundreds of specific mental abilities but some can be measured accurately and are reliable predictors of academic and financial success.
IQ test also better for an adult, whether for entertaining (exercise their brain) to get personality and intelligence level or to decide which careers, jobs, or professions match their IQ and intelligence. Many of accurate IQ test and personality intelligence tests online, Everyone has hundreds of specific mental abilities but some can be measured accurately and are reliable predictors of academic and financial success.Something everyone should take IQ score once in their life, at least to compare their mental strengths and weaknesses. Valid and accurate IQ test will give and help them personalized relationship advice and career advice.
Hipocampo (cerebro)
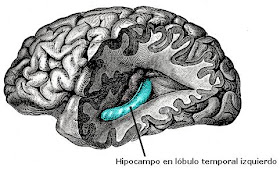
Perspectiva del hipocampo desde la cara inferior del cerebro

Wednesday, June 9, 2010
Vitamin and Mineral Supplements for Pregnancy

Certain conditions or habits of the pregnant woman may increase requirements fo certain nutrients. For example, women who are carryng more than one fetus or who smoke cigarettes, drink alcohol, or use illicit drugs may require additional supplementation. Special attention also needs to be given to the adequacy of calcium and vitamin D intake for pregnant women younger than 25 years, because their bon mineral density is still increasing (Institute of medicine 1990). Calcium Supplements might be advised for women who drink little or no milk, and Vitamin B12 might be needed by the vegan who eats no animal protein (Williams, 1993). If any vitamin or mineral supplements are used, it is important for the woman to understand that these are in addition to, not stead of, her recommended dietary intake
(taken From Assesment and Management in the Antepartum Period Book)
Related Post
Latencia
El período de latencia representa una etapa de detención en la evolución de la sexualidad. Durante él se observa, desde este punto de vista, una disminución de las actividades sexuales, la desexualización de las relaciones de objeto y de los sentimientos, especialmente el predominio de la ternura sobre los deseos sexuales, y la aparición de sentimientos como el pudor y el asco y de aspiraciones morales y estéticas. Según la teoría psicoanalítica, el período de latencia tiene su origen en la declinación del complejo de Edipo; corresponde a una intensificación de la represión, la cual provoca una amnesia que abarca los primeros años, y una transformación de las catexis de objetos en identificaciones con los padres y un desarrollo de las sublimaciones.
Tuesday, June 8, 2010
Ncp - Nursing Care Plan Patient Heart Failure

NCP for Heart Failure
Assessment
- Left-sided heart failure ; Dyspnea, Crackles, Orthopnea, Paroxysmal noctural dyspnea, Tachypnea, Tachycardia, Gallop rhythm (third or S3 and fourth or S4 heart sound), Fatigue, Anxiety, Arrhythmias and Cough.
- Righ-sided heart failure ; Dependent edema, Weight gain, Fatique, Jugular vein distention, Tachycardia, Gallop rhythm (S3 or S4), Nausea, Anorexia, Hepatomegaly and Ascites.
Nursing Diagnoses
- Excess fluid volume
- Activity intolerance
- Ineffective health maintenance
Planing and Goals of Nursing Care
- The clients will understand how to cope with necessary lifestyle changes.
- The client won't develop preventable complication
- The client will will understand how to continue therapy at home.
Nursing Intervention For Heart Failure
- Assess cardiovascular status, vital sign and hemodynamic variable to detect signs of reduced cardiac output.
- Assess respiratory status to detect increasing fluid in the lungs and respiratory failure.
- Keep the client in semi-fowler's position to increase chest expansion and improve ventilation.
- Administer medication as prescribed, to enhance cardiac performance and reduce excess fluids.
- Administer oxygen to enhance arterial oxygenation.
- Measure and record intake and output, Intake greater than output may indicated fluid retention.
- Monitor laboratory test result to detect electrolyte imbalances, renal failure, and impaired cardiac circulation.
- Provide suctioning, if necessary assist with turning and encourage coughing and deep breathing to prevent pulmonary complication.
- Restrict oral fluid to avoid worsening the client's condition.
- Weigh the client daily to detect fluid retention. A weight gain of 2lb (0,9 kg) in 1 day or 5 lb (2,3 kg) in 1 week indicates fluid gain.
- Measure and record the client's abdominal girth. An increased in abdominal girht suggests worsening fluid retention and right-sided heart failure.
- Make sure the client maintains a low-sodium diet to reduce fluid accumulation.
- Encourage the client to express feelings, such as a fear of dying to reduce anxiety.
Disforia
La disforia también puede aparecer como un efecto colateral de los medicamentos antipsicóticos para tratar la esquizofrenia y sus síntomas.
Monday, June 7, 2010
NCLEX (National Council Licensure EXamination)
NCLEX examinations are developed and owned by the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc. (NCSBN). NCSBN administers these examinations on behalf of its member boards which consist of the boards of nursing in the 50 states, the District of Columbia, and four U.S. territories American Samoa, Guam, Northern Mariana Islands and the Virgin Islands.
To ensure public protection, each board of nursing requires a candidate for licensure to pass the appropriate NCLEX examination, NCLEX-RN for registered nurses and the NCLEX-PN for vocational/practical nurses. NCLEX examinations are designed to test the knowledge, skills and abilities essential to the safe and effective practice of nursing at the entry-level.
NCLEX examinations are provided in a computerized adaptive testing (CAT) format and are presently administered by Pearson VUE in their network of Pearson Professional Centers (PPC).
From : http://en.wikipedia.org
Neurolépticos
Ambos tipos de antipsicóticos, los típicos y los atípicos, tienden a bloquear los receptores de la vía de la dopamina en el cerebro. Algunos efectos colaterales incluyen la ganancia de peso, agranulocitosis, discinesia y acatisia tardía. Entre los neurolépticos más conocidos figuran: haloperidol, clorpromazina, flufenazina, risperidona, quetiapina, aripiprazol, y clozapina.
Farmacología de los neurolépticos
La farmacología de los antipsicóticos clásicos es la siguiente: 1) son eficaces sobre los síntomas positivos de la esquizofrenia; 2) su acción antipsicótica se ejerce al bloquear los receptores dopaminérgicos D2; 3) tienen muchos efectos adversos, sobre todo extrapiramidales. Antipsicóticos atípicos: 1) su acción antipsicótica se ejerce no sólo por el antagonismo de los receptores dopaminérgicos D2, sino también por los de serotonina, histamínicos y muscarínicos; 2) presentan un espectro de eficacia mayor, incluyendo los síntomas negativos y positivos; 3) ocasionan menos efectos adversos incluyendo una baja incidencia de efectos extrapiramidales, además de una mínima afectación de la prolactina y otras hormonas.
Discinesia
Sunday, June 6, 2010
Gonorrhea Treatment

Gonorrhea Treatment
by: Mary Chris
A Positive test for a sexually transmitted disease is not fun. The information can hit you hard and everyone reacts in a different way. The worse the disease the worst feeling you must have. There is nothing nice about getting a positive test result for sexually transmitted disease. If you are looking to avoid this sort of thing, maybe you should consider treatment immediately. In regards to Gonorrhea Treatment, there is good news. The disease is easy to treat and is not going to be some crazy experiment in regards to helping you. The most important thing you can do is to make sure that you see a doctor when symptoms appear and get yourself some medicine fast. This is going to be your friend in regards to treating and getting cured of this disease that is ultimately preventable.
Gonorrhea Treatment is not crazy. It is easy to get access to medicine, just simply go to a doctor and get this taken care of. You are going to get an antibiotic medicine to help this. It can either be a pill or an injection and most of the times a single dose is going to cure you. However, some antibiotic treatments do last several days and are not too crazy to apply. Some medicines are not easily given to pregnant women, so you should be careful and make sure you tell your doctor.
Do not wait to get treated. If you wait to get treated and are looking for Gonorrhea Treatment, then you are going to make things very complicated. You are going to have problems with reproduction, and even have some potentially life threatening problems. You really need to be aware of how bad things can get if you do not get access to proper medical attention. This is not complicated, and it is your goal to get yourself a proper physician to help you. You need to get tested for this immediately if you have doubts, and get yourself a good Gonorrhea Treatment.
If you are getting tested and seeking Gonorrhea Treatment, then also make sure you get tested for other sexually transmitted diseases. You do not want to be one of those people that end up with being a statistic. Statistics are important, but you don't need to be on the bad side, you would probably do a lot better on the positive end of the spectrum. Seriously, have a good day in the sun by getting yourself treated and cured of anything potentially harmful. If you detect your illness early, it can be a memory and a lesson learned. Use your head and protect yourself in regards to sex. Do not go around having sex with many partners and lack discretion, because that is a really sad scenario. You have been warned and you can get Gonorrhea Treatment easily. So do not just wish it away, get yourself treated early and detect any other diseases while you're at it. The best advice you can get in regards to sexually transmitted diseases is protection. Use protection, use discretion and live happy.
I have made a Gonorrhea Treatment Blog in order to assist victims of STD Gonorrhea.
www.e-healtharticles.comhttp://purba-java.blogspot.com/2010/04/gonorrhea-treatment.html
Saturday, June 5, 2010
Immunizations During Pregnancy
Pregnant women with chronic cardiac, pulmonary, or metabolic diseases should be evaluated carefully for immunization against influenza and pneumonia.
The nurse advises the pregnant women to minimize expsure to infectious diseases when travelling. Any febrile illness or rash should be reported to the physicians without delay.
Clients are educated about updating immuzations after delivery to reduce future risk. After receiving live organism vaccinations, clients are advised to avoid conception for recommended time.
Taken from : assesment and management in the antepartum period book
http://purba-java.blogspot.com/2010/05/immunizations-during-pregnancy.html
Acatisia
La acatisia se da como resultado de los efectos colaterales de los neurolépticos. Fármacos como la metoclopramida también pueden provocar este efecto adverso. En menor grado, la acatisia también puede ser un síntoma de la enfermedad de Parkinson. Se debe hacer el diagnóstico diferencial con el "síndrome de las piernas inquietas", en el cual lo que sucede es que los movimientos se exacerban con el reposo, suelen aparecer al acostarse, y ceden con el movimiento.
University of Phoenix
University of Phoenix
The University of Phoenix offers a variety nursing programs to fit the needs of all students. The curriculum is built upon a foundation of biological, physical and social sciences which contribute to the science of nursing. Choose from a campus near you.
Visit Sites : University of Phoenix
Chamberlain College of Nursing - Online RN to BSN Program / Online MSN Program
Online RN to BSN Program / Online MSN Program
Chamberlain College of Nursing
Over 120 years of excellence in nursing education.
Chamberlain offers:
- Career mobility and advancement
- Financial aid programs, employer tuition reimbursement and payment plans may also be available
- Rolling admissions all year in January, March, May, July, September and November
- Personal, student-focused learning
- Top-notch, degreed faculty
- Flexible online classes
- Proven nursing/health care education model
Fast-Track RN to BSN Online Degree Completion Program
Take your nursing career to a whole new level. Advance your career by completing your BSN degree online, while you work!
This flexible online program allows registered nurses to advance their nursing careers by earning a BSN degree in as few as 3 semesters.

- Fast track: RNs can earn a BSN degree by completing just 3 semesters
- Flexibe: All courses are offered online - 8 week sessions
- Generous transfer credit opportunities: RNs with an unrestricted license may receive over 80 transfer credit hours toward a BSN degree
- Portfolio credits: Students may receive up to 8 additional credit hours of coursework based on professional work experience
Regardless of your busy lifestyle, you can fulfill your personal and career goals to earn your BSN degree through Chamberlain College of Nursing.
Select a Campus: Online
Friday, June 4, 2010
Quetiapina
Farmacocinética

Kaplan University - School of Nursing
School of Nursing
6301 Kaplan University Avenue
Fort Lauderdale, FL 33309
Kaplan University
Kaplan University offers a broad selection of programs that focus on the career goals of working adults from a variety or professional disciplines. Emphasis is on real-world knowledge and skill development, and Kaplan University offers programs designed to provide the concepts and techniques you can use to pursue your professional and educational goals.*
Kaplan University gives you the control to study on your own schedule. There are no job interruptions, travel expenses, or hours spent searching the campus map. Study anytime and anywhere you have an Internet connection. The flexibility and dynamic interaction of online education at Kaplan University also allows for innovative Web-based learning opportunities via message boards, online readings, academic exercises, and Web Field Trips.
Kaplan University is regionally accredited. Visit our website for details.
Kaplan University proudly offers reduced tuition rates for active-duty military personnel, military spouses, and military veterans.
Thursday, June 3, 2010
Neurosis
En la neurosis el sujeto mantiene un adecuado nivel de introspección y conexión con la realidad, pero presenta la necesidad de desarrollar conductas repetitivas y en muchos casos inadaptativas con objeto de disminuir el nivel de estrés. Se trata, en realidad, de un rasgo característico que acompaña al sujeto durante toda su vida, de gravedad muy variable, desde grados leves y controlables hasta situaciones gravemente incapacitantes que pueden llegar a precisar hospitalización.
Sigmund Freud desarrolló diversos trabajos en relación con la histeria y los trastornos obsesivos, publicados entre 1892 y 1899, sentando las bases psicogénicas de lo que él denominó psiconeurosis. A partir de sus trabajos se elaboró una clasificación, ya en desuso, que distinguía varios tipos de neurosis en función de la expresión final de los síntomas provocados por el síntoma nuclear de la angustia: neurosis de angustia, neurosis fóbicas, neurosis obsesivo-compulsivas, neurosis depresivas, neurosis neurasténicas, neurosis de despersonalización, neurosis hipocondríacas y neurosis histéricas.
Wednesday, June 2, 2010
NCLEX Practice Questions
A. Sulfasalazine
B. Levodopa
C. Phenolphthalein
D. Aspirin
2. You are responsible for reviewing the nursing unit's refrigerator. If you found the following drug in the refrigerator it should be removed from the refrigerator's contents?
A. Corgard
B. Humulin (injection)
C. Urokinase
D. Epogen (injection)
3. A 34 year old female has recently been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease. She has also recently discovered that she is pregnant. Which of the following is the only immunoglobulin that will provide protection to the fetus in the womb?
A. IgA
B. IgD
C. IgE
D. IgG
4. A second year nursing student has just suffered a needlestick while working with a patient that is positive for AIDS. Which of the following is the most important action that nursing student should take?
A. Immediately see a social worker
B. Start prophylactic AZT treatment
C. Start prophylactic Pentamide treatment
D. Seek counseling
5. A thirty five year old male has been an insulin-dependent diabetic for five years and now is unable to urinate. Which of the following would you most likely suspect?
A. Atherosclerosis
B. Diabetic nephropathy
C. Autonomic neuropathy
D. Somatic neuropathy
6. You are taking the history of a 14 year old girl who has a (BMI) of 18. The girl reports inability to eat, induced vomiting and severe constipation. Which of the following would you most likely suspect?
A. Multiple sclerosis
B. Anorexia nervosa
C. Bulimia
D. Systemic sclerosis
7. A 24 year old female is admitted to the ER for confusion. This patient has a history of a myeloma diagnosis, constipation, intense abdominal pain, and polyuria. Which of the following would you most likely suspect?
A. Diverticulosis
B. Hypercalcaemia
C. Hypocalcaemia
D. Irritable bowel syndrome
8. Rho gam is most often used to treat____ mothers that have a ____ infant.
A. RH positive, RH positive
B. RH positive, RH negative
C. RH negative, RH positive
D. RH negative, RH negative
9. A new mother has some questions about (PKU). Which of the following statements made by a nurse is not correct regarding PKU?
A. A Guthrie test can check the necessary lab values.
B. The urine has a high concentration of phenylpyruvic acid
C. Mental deficits are often present with PKU.
D. The effects of PKU are reversible.
10. A patient has taken an overdose of aspirin. Which of the following should a nurse most closely monitor for during acute management of this patient?
A. Onset of pulmonary edema
B. Metabolic alkalosis
C. Respiratory alkalosis
D. Parkinson's disease type symptoms
11. A fifty-year-old blind and deaf patient has been admitted to your floor. As the charge nurse your primary responsibility for this patient is?
A. Let others know about the patient's deficits
B. Communicate with your supervisor your concerns about the patient's deficits.
C. Continuously update the patient on the social environment.
D. Provide a secure environment for the patient.
12. A patient is getting discharged from a SNF facility. The patient has a history of severe COPD and PVD. The patient is primarily concerned about their ability to breath easily. Which of the following would be the best instruction for this patient?
A. Deep breathing techniques to increase O2 levels.
B. Cough regularly and deeply to clear airway passages.
C. Cough following bronchodilator utilization
D. Decrease CO2 levels by increase oxygen take output during meals.
13. A nurse is caring for an infant that has recently been diagnosed with a congenital heart defect. Which of the following clinical signs would most likely be present?
A. Slow pulse rate
B. Weight gain
C. Decreased systolic pressure
D. Irregular WBC lab values
14. A mother has recently been informed that her child has Down's syndrome. You will be assigned to care for the child at shift change. Which of the following characteristics is not associated with Down's syndrome?
A. Simian crease
B. Brachycephaly
C. Oily skin
D. Hypotonicity
15. A patient has recently experienced a (MI) within the last 4 hours. Which of the following medications would most like be administered?
A. Streptokinase
B. Atropine
C. Acetaminophen
D. Coumadin
16. A patient asks a nurse, “My doctor recommended I increase my intake of folic acid. What type of foods contain folic acids?”
A. Green vegetables and liver
B. Yellow vegetables and red meat
C. Carrots
D. Milk
17. A nurse is putting together a presentation on meningitis. Which of the following microorganisms has noted been linked to meningitis in humans?
A. S. pneumonia
B. H. influenza
C. N. meningitis
D. Cl. difficile
18. A nurse is administering blood to a patient who has a low hemoglobin count. The patient asks how long to RBC's last in my body? The correct response is.
A. The life span of RBC is 45 days.
B. The life span of RBC is 60 days.
C. The life span of RBC is 90 days.
D. The life span of RBC is 120 days.
19. A 65 year old man has been admitted to the hospital for spinal stenosis surgery. When does the discharge training and planning begin for this patient?
A. Following surgery
B. Upon admit
C. Within 48 hours of discharge
D. Preoperative discussion
20. A child is 5 years old and has been recently admitted into the hospital. According to Erickson which of the following stages is the child in?
A. Trust vs. mistrust
B. Initiative vs. guilt
C. Autonomy vs. shame
D. Intimacy vs. isolation
21. A toddler is 16 months old and has been recently admitted into the hospital. According to Erickson which of the following stages is the toddler in?
A. Trust vs. mistrust
B. Initiative vs. guilt
C. Autonomy vs. shame
D. Intimacy vs. isolation
22. A young adult is 20 years old and has been recently admitted into the hospital. According to Erickson which of the following stages is the adult in?
A. Trust vs. mistrust
B. Initiative vs. guilt
C. Autonomy vs. shame
D. Intimacy vs. isolation
23. A nurse is making rounds taking vital signs. Which of the following vital signs is abnormal?
A. 11 year old male – 90 b.p.m, 22 resp/min., 100/70 mm Hg
B. 13 year old female – 105 b.p.m., 22 resp/min., 105/60 mm Hg
C. 5 year old male- 102 b.p.m, 24 resp/min., 90/65 mm Hg
D. 6 year old female- 100 b.p.m., 26 resp/min., 90/70mm Hg
24. When you are taking a patient's history, she tells you she has been depressed and is dealing with an anxiety disorder. Which of the following medications would the patient most likely be taking?
A. Elavil
B. Calcitonin
C. Pergolide
D. Verapamil
25. Which of the following conditions would a nurse not administer erythromycin?
A. Campylobacterial infection
B. Legionnaire's disease
C. Pneumonia
D. Multiple Sclerosis
Answer Key
1. D
2. A
3. D
4. B
5. C
6. B
7. B
8. C
9. D
10. D
11. D
12. C
13. B
14. C
15. A
16. A
17. D
18. D
19. B
20. B
21. A
22. D
23. B
24. A
25. D
Aripiprazol
Dosificación: el aripiprazol está disponible en tabletas de 2mg, 5mg, 10mg, 15mg, 20mg, y 30mg. También esta disponible en tabletas orodispersables de 10 y 15 mg, en soluciones de 1mg/1ml e inyecciones de 7.5mg/ml para efecto rápido.
Farmacocinética
El aripiprazol posee una biodisponibilidad del 87% en los comprimidos orales, sufriendo una amplia metabolización hepática: deshidrogenación, hidroxilación y N-dealquilación. Este fármaco presenta una cinética lineal y tiene una vida media de aproximadamente 75 horas. La concentración en plasma en estado estacionario se logra en unos 14 días. Su metabolito principal activo es el dehidro-aripiprazol, cuya vida media de eliminación es de unas 94 horas. El dehidro-aripiprazol se acumula típicamente en una proporción del 40% de la concentración de aripiprazol. El farmaco de administración parenteral se excreta solo en trazas, y sus metabolitos, activos o no, se excretan por vía fecal y orina. El aripiprazol se metaboliza por el citocromo P450 isoenzima 3A4 y 2D6. Debido a ello, la coadministración de aripiprazol con medicamentos que puedan inhibirlo, como la paroxetina o la fluoxetina, o inducirlo, como la carbamazepina, pueden aumentar o disminuir las concentraciones plasmáticas del aripiprazol.
Farmacología del aripiprazol
El mecanismo de acción del aripiprazol es diferente de los de otros antipsicóticos atípicos, como ser la clozapina, olanzapina, quetiapina, ziprasidona y risperidona. El aripiprazol ejerce sus efectos antipsicóticos en principio por agonismo parcial del receptor D2, del que se ha visto que modula la actividad dopaminérgica en áreas donde la actividad de la dopamina se puede incrementar o disminuir, como las áreas mesolímbica y mesocortical del cerebro esquizofrénico, respectivamente. Además de su acción agonista parcial del receptor D2, el aripiprazol también es un agonista parcial del receptor 5-HT1A y como otros antipsicóticos atípicos muestra un perfil antagonista del receptor 5-HT2A.

