NCP - Nursing Care Plan for Child with Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus
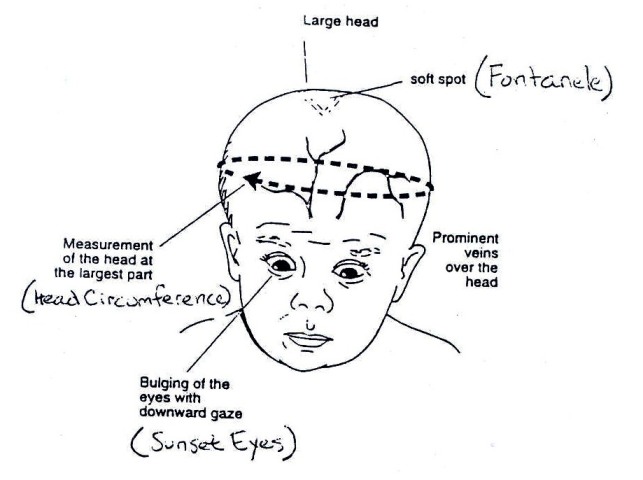
The term hydrocephalus is derived from the Greek words "hydro" meaning water and "cephalus" meaning head. As the name implies, it is a condition in which the primary characteristic is excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain. Although hydrocephalus was once known as "water on the brain," the "water" is actually cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) — a clear fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. The excessive accumulation of CSF results in an abnormal widening of spaces in the brain called ventricles. This widening creates potentially harmful pressure on the tissues of the brain.
The ventricular system is made up of four ventricles connected by narrow passages.. Normally, CSF flows through the ventricles, exits into cisterns (closed spaces that serve as reservoirs) at the base of the brain, bathes the surfaces of the brain and spinal cord, and then reabsorbs into the bloodstream.
CSF has three important life-sustaining functions :
- to keep the brain tissue buoyant, acting as a cushion or "shock absorber";
- to act as the vehicle for delivering nutrients to the brain and removing waste; and
- to flow between the cranium and spine and compensate for changes in intracranial blood volume (the amount of blood within the brain).
The balance between production and absorption of CSF is critically important. Because CSF is made continuously, medical conditions that block its normal flow or absorption will result in an over-accumulation of CSF. The resulting pressure of the fluid against brain tissue is what causes hydrocephalus.
www.medicinenet.com
Clinical manifestations :
- Enlarging head circumference
- Irritable, lethargic, apathetic
- Convergent strabismus
- Increased Intra-cranial pressure, decreased consciousness
- Fontanels: tense; bulging
- Manifestation appropriate location in the brain lesions.
Assessment
- Medical history: cerebral trauma, cerebral infections, etc.
- Physical examination: a focus area of the head
- Inspection psychomotor
- Other clinical manifestations
- Check diagnostic
Nursing Diagnosis
- The risk of injury related to increased intra-cranial pressure
- The risk of infection related to mechanical drainage installed
- Changes in tissue perfusion related to interruption of blood flow
- The risk of skin integrity related disorders with an emphasis on the area behind the head
- Impaired family processes related to situational crises (children with physical disorders)
Nursing Intervention
The risk of injury associated with increased intra-cranial pressure
- Observation of Increased intra cranial pressure
- Perform neurological assessment
- Position the patient with safe, elevate the head area
- Avoid the use of sedation.














No comments:
Post a Comment